
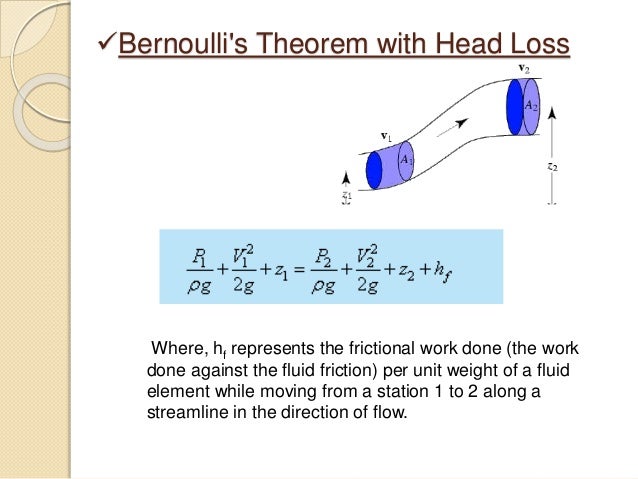
The Bernoulli equation can be considered to be the conservation of energy principle for the flowing fluids. Bernoulli’s Principle Formulaīernoulli’s equation formula is considered a relation between pressure, potential energy, and kinetic energy of a fluid.
This happens with a decrease in the potential energy (the static pressure and internal energy). While all the energy remains constant, an increase in the fluid velocity will imply that there is an increase in the kinetic energy or dynamic pressure. In case of steady flow, the sum of energy forms in a fluid will remain the same at all points of that streamline. By using incompressible flow, we will have the simplest form of Bernoulli’s equation What is Bernoulli’s Principle ?īernoulli’s principle states that an increase in the velocity (the speed of a fluid) occurs simultaneously and must be accompanied by a decrease in the potential energy of the fluid (or the static pressure).īernoulli’s principle can be derived from the conservation of energy principle. Incompressible flows are gasses and gasses with a low Mach number and constant fluid density, regardless of the pressure flow.

The streamline in steady flow is the path traced by a single particle within the fluid. Or simply, the Bernoulli equation states that the sum of the potential, kinetic, and flow energies of a fluid is constant in a streamline in steady flow. The constant is called the total pressure of the flow (pt).
#Bernoulli principle gases plus#
It states that the dynamic pressure plus the static pressure in the flow, one half of the density (r) times the velocity (V) squared, is equal to a constant throughout the flow. P is the static pressure (the pressure of the fluid)īernoulli’s theorem describes the relation between velocity, pressure, and elevation of a flowing fluid in a streamline. Other Applications of Bernoulli’s Principle.Application of Bernoulli’s equation in medicine.Application of Bernoulli’s Theorem in Aeroplanes.Application of Bernoulli’s equation in pumps.Bernoulli Theorem application in fluid mechanics.Limitations on the Use of Bernoulli Theorem.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
